Inception layers
Horizontal scaling for Ethereum
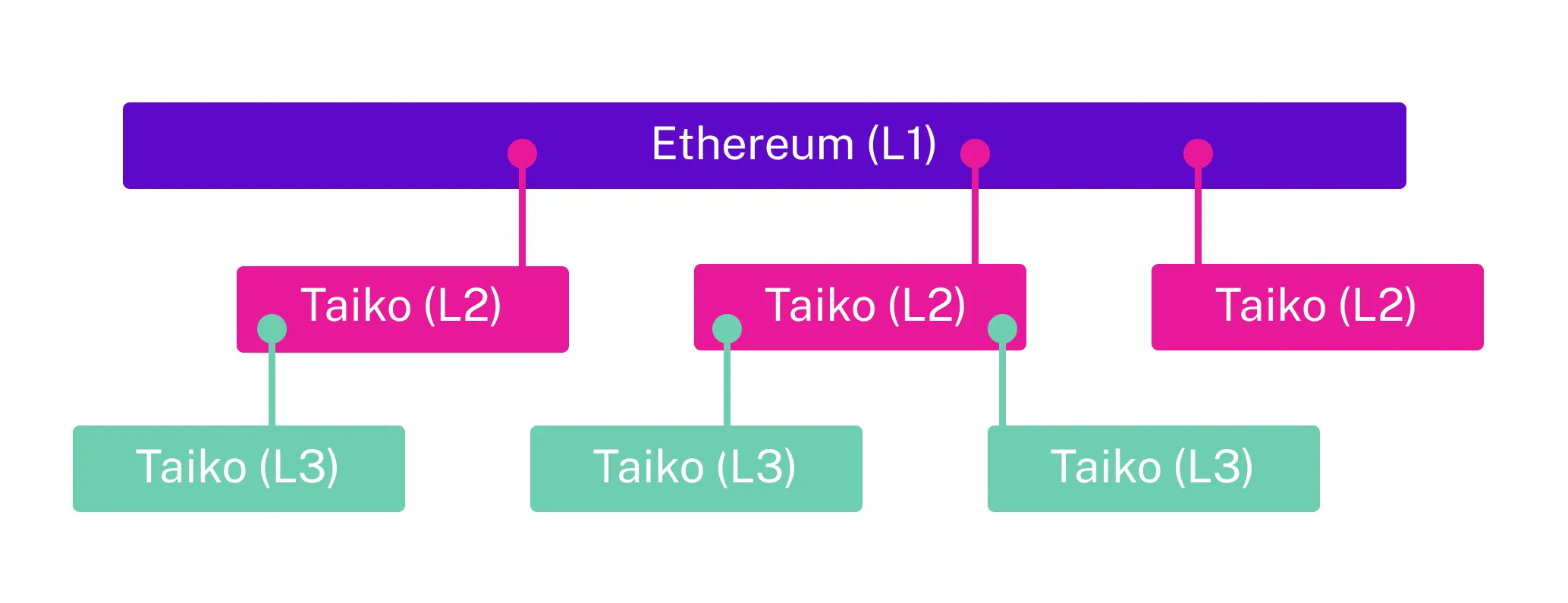
To scale Ethereum you need more than one rollup. Taiko’s design is flexible so that it can run multiple instances of Taiko as parallel L2s, but it also has the option of running Taiko on Taiko as an L3. This was trivial to do because Taiko is Ethereum-equivalent.
Inception layers
Inception layers refer to using Taiko as an L2 and deploying the exact codebase as an L3 on top. Given Taiko’s Ethereum-equivalence, the L3 to L2 relationship maps closely to the L2 to L1 relationship, offering maximum reusability and simplicity.
This is needed because a single rollup can only scale Ethereum so far before state bloat becomes a problem. Multiple rollups (L2/L3/L-) are required for Ethereum at great scale. Inception layers (reusing the same type-1 codebase) unlock extremely extensible scalability for Ethereum.
Further, Ethereum-equivalence across L2s, L3s, and beyond means inheriting some powerful properties, like built-in arbitrary message passing. This follows from the ability for one type-1 to read Merkle proofs from another. This combats a downside of having multiple chains: fears of fragmentation degrading the UX/DevX. With the different layers (adjacent and atop) easily able to speak to each other using Merkle proofs, a fragmented outcome can be avoided.
For more information on how Taiko’s message passing works see the concept page on Bridging.