Taiko Alethia nodes
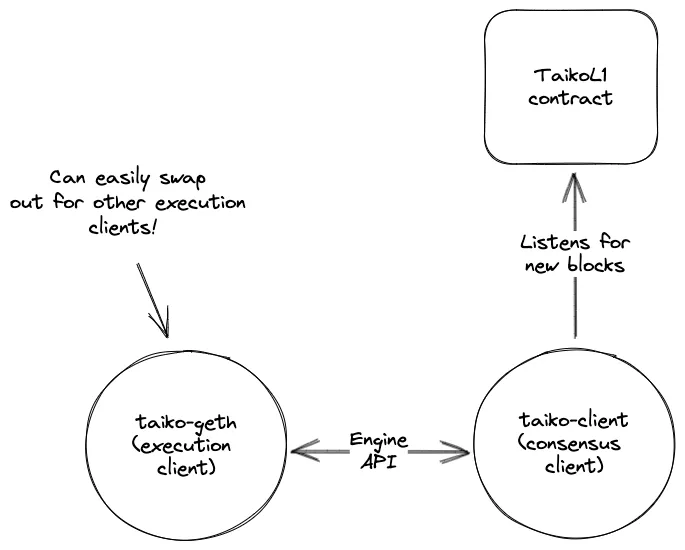
Taiko Alethia nodes are minimally modified Ethereum execution clients that adhere to Ethereum’s execution-consensus separation model. The two primary components of a Taiko node are:
- taiko-geth (execution client)
- taiko-client (consensus client)
This architecture mirrors Ethereum’s execution/consensus split but replaces the consensus layer with Taiko’s own taiko-client. The taiko-client drives taiko-geth over the Engine API, allowing modular execution client compatibility.
Execution Layer: taiko-geth
Section titled “Execution Layer: taiko-geth”taiko-geth is a fork of go-ethereum with minimal changes to support Taiko Alethia.
Functionality:
Section titled “Functionality:”- Processes and executes L2 transactions from the Taiko mempool.
- Maintains state storage, transaction history, and receipts.
- Implements Ethereum-equivalence, ensuring all EVM opcodes behave identically.
- Supports modular execution by allowing future execution clients.
All modifications to go-ethereum can be reviewed in the Geth fork diff.
Consensus Layer: taiko-client
Section titled “Consensus Layer: taiko-client”taiko-client acts as the consensus component, replacing Ethereum’s traditional beacon chain. It interfaces with taiko-geth using the Engine API.
Components:
Section titled “Components:”driver
Section titled “driver”- Serves as the L2 consensus client.
- Monitors L1 events from TaikoInbox to detect proposed batches.
- Directs the execution engine to insert or reorganize blocks through the Engine API.
proposer
Section titled “proposer”- Collects pending transactions from
taiko-geth’s txpool. - Constructs batch-compliant txLists and submits them to TaikoInbox.
prover
Section titled “prover”- Fetches proposed batches from
TaikoInboxand verifies them. - Generates ZK/Secure Enclave proofs to validate state transitions.
Chain Synchronization Process
Section titled “Chain Synchronization Process”The Taiko Alethia consensus model differs from Ethereum’s due to its rollup-based structure.
- Driver Initialization
- Fetches the latest verified L2 head from
TaikoInbox. - Tries to sync state via P2P.
- If P2P sync fails, inserts verified L2 blocks sequentially using the Engine API.
- After catching up to the latest verified L2 block, proceeds to the following step.
- Fetches the latest verified L2 head from
- Batch Proposal Ingestion
- Listens for
TaikoInbox.BatchProposedevents. - Retrieves the transaction calldata from
TaikoInbox.proposeBatch. - Decompresses
txListBytesand reconstructs blocks shared metadata.
- Listens for
- Validation and Execution
- If
txListis valid, constructs an L2 anchor transaction and inserts the block. - If
txListis invalid, constructs an empty L2 block.
- If
Batch Proposal Process
Section titled “Batch Proposal Process”-
The proposer fetches pending transactions from
taiko-geth. -
If transaction volume exceeds the max txList size, transactions are split into batches.
-
The proposer submits
TaikoInbox.proposeBatchtransactions, encoding thetxList.
Batch Proving Process
Section titled “Batch Proving Process”Once a batch is proposed:
-
The prover retrieves the corresponding TaikoInbox.proposeBatch transaction calldata.
-
It waits until the L2 execution engine has inserted the blocks.
-
The prover generates a validity proof.
For a valid or invalid txList, the prover:
-
Constructs a Merkle proof verifying the block’s txRoot.
-
Verifies the TaikoAnchor.anchorV3 transaction in the Merkle Patricia Trie (MPT).
-
Submits:
TaikoAnchor.anchorV3transaction’s RLP-encoded bytes.- Merkle proofs.
- Proof-of-validity to
TaikoInbox.proveBatches.
Even if the txList is invalid, proving ensures that invalid blocks are mapped to an empty anchor-only block.
Taiko Alethia Node APIs
Section titled “Taiko Alethia Node APIs”A Taiko Alethia node exposes Ethereum-equivalent JSON-RPC methods, making it compatible with standard Ethereum tooling.
Differences from Ethereum Geth
Section titled “Differences from Ethereum Geth”-
Modified Consensus Rules: Taiko uses
taiko-clientinstead of a traditional beacon chain. -
Blob Data Handling: If EIP-4844 blobs are enabled, calldata is stored separately.
-
Taiko-Specific Events: Includes
TaikoInbox.BatchProposed,TaikoInbox.BatchesVerified, etc.
For a complete diff, check the Geth fork comparison.
JSON-RPC API
Section titled “JSON-RPC API”Supports all standard Ethereum execution APIs. See Ethereum Execution API Docs.
Engine API
Section titled “Engine API”Manages consensus-execution communication. See Engine API Spec.
Hive Test Compliance
Section titled “Hive Test Compliance”Taiko Alethia aims to pass the Ethereum Hive e2e test suite, ensuring API and execution consistency.