Inception layers
Ethereum’s scalability challenges cannot be fully solved with a single rollup. A single L2 can only process a finite number of transactions before state bloat and sequencer bottlenecks emerge. To truly scale Ethereum, multiple rollups need to operate in parallel and in stacked layers.
Taiko Alethia is designed with flexibility, enabling:
- Parallel L2s: Multiple independent rollup instances running side by side.
- Recursive Rollups (L3s on L2s): Running Taiko on Taiko, deploying the same architecture on top of itself.
What Are Inception Layers?
Section titled “What Are Inception Layers?”Inception layers refer to a recursive rollup approach where Taiko Alethia operates as an L2, and the exact same Taiko Alethia codebase is deployed as an L3 on top of it. Since Taiko Alethia is Ethereum-equivalent, the relationship between L3 → L2 closely mirrors that of L2 → L1. This maintains a high degree of reusability and interoperability.
Why Are Inception Layers Needed?
Section titled “Why Are Inception Layers Needed?”-
Ethereum’s Scaling Limits
A single L2 has inherent constraints:
- Throughput bottlenecks: Even a performant rollup has an upper bound on TPS.
- State Growth: Storing all state in a single rollup leads to expensive calldata and verification costs on Ethereum L1.
- Multiple Rollups Are the Future
- The Ethereum roadmap anticipates a multi-rollup ecosystem.
- Inception layers allow for seamless rollup interoperability.
- Unlocking Extensible Scalability
- Multiple Taiko L2 instances can scale horizontally.
- Multiple L3 instances on top of L2 scale vertically (stacked rollups).
- L3s inherit the same security model as L2s, ensuring trustless execution.
Benefits of Inception Layers
Section titled “Benefits of Inception Layers”-
Ethereum-Equivalence Across Layers
- L2s and L3s share the same execution environment as Ethereum.
- Developers can reuse smart contracts across layers without modifications.
- EVM compatibility is preserved, ensuring seamless migration.
-
Optimized for Composability & Interoperability
- Rollups at different layers can efficiently interact using Merkle proofs.
- This enables secure, trustless message passing between L1, L2, and L3.
-
Mitigating UX Fragmentation
- A major downside of a multi-rollup world is liquidity fragmentation and complex cross-chain UX.
- Taiko’s inception layers combat this by using built-in arbitrary message passing.
- One rollup can natively read Merkle proofs from another, avoiding fragmented liquidity.
Inception Layers Architecture
Section titled “Inception Layers Architecture”Multi-Layer Rollup Structure
Section titled “Multi-Layer Rollup Structure”The following illustrates how Ethereum, Taiko L2, and Taiko L3 layers interconnect:
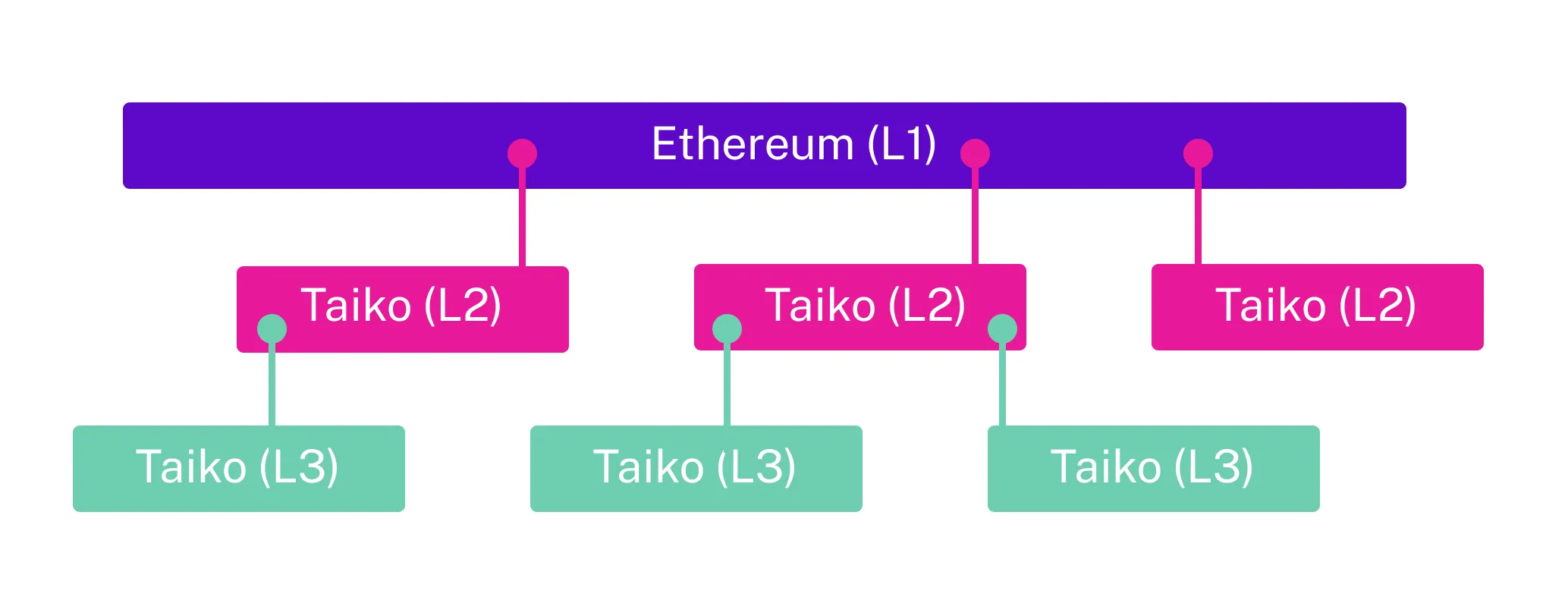
- Ethereum L1 serves as the base layer for settlement and data availability.
- Multiple Taiko L2s operate in parallel, processing transactions independently.
- Recursive Taiko L3s are deployed on top of L2s, allowing for additional scalability.
Built-in Message Passing Between Layers
Section titled “Built-in Message Passing Between Layers”Ethereum-equivalence across L2s, L3s, and beyond means native arbitrary message passing. This is achieved via:
- Merkle Proofs: Enabling trustless state validation across rollups.
- Cross-Layer Communication Protocols: Ensuring frictionless interoperability.
Further Reading
Section titled “Further Reading”For more details on cross-layer communication, refer to the Bridging documentation.